Osteoarthritis
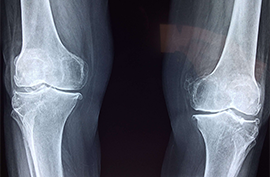
Osteoarthritis, often referred to as "wear and tear" arthritis, is a chronic joint condition that primarily affects the cartilage—the protective tissue that cushions the ends of bones in joints. As cartilage deteriorates over time, bones may begin to rub against each other, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. This condition commonly develops in weight-bearing joints such as the knees, hips, and spine, but can also affect the hands and other joints. While aging is a significant risk factor, other factors such as obesity, joint injuries, and genetic predisposition can contribute to its onset.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis usually develop gradually and worsen over time. Individuals may experience pain during or after movement, stiffness after periods of inactivity, swelling around the joint, and a decreased range of motion. These symptoms can vary in severity, impacting daily activities and quality of life. Diagnosis typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies such as X-rays.
Management of osteoarthritis focuses on relieving symptoms, improving joint function, and slowing the progression of the disease. Treatment options may include medications to reduce pain and inflammation, lifestyle modifications such as weight management and exercise, physical therapy, and in some cases, surgery to repair or replace damaged joints. While osteoarthritis is a chronic condition without a cure, early diagnosis and appropriate management strategies can help individuals maintain an active lifestyle and manage their symptoms effectively.

